LKL
Mechanism
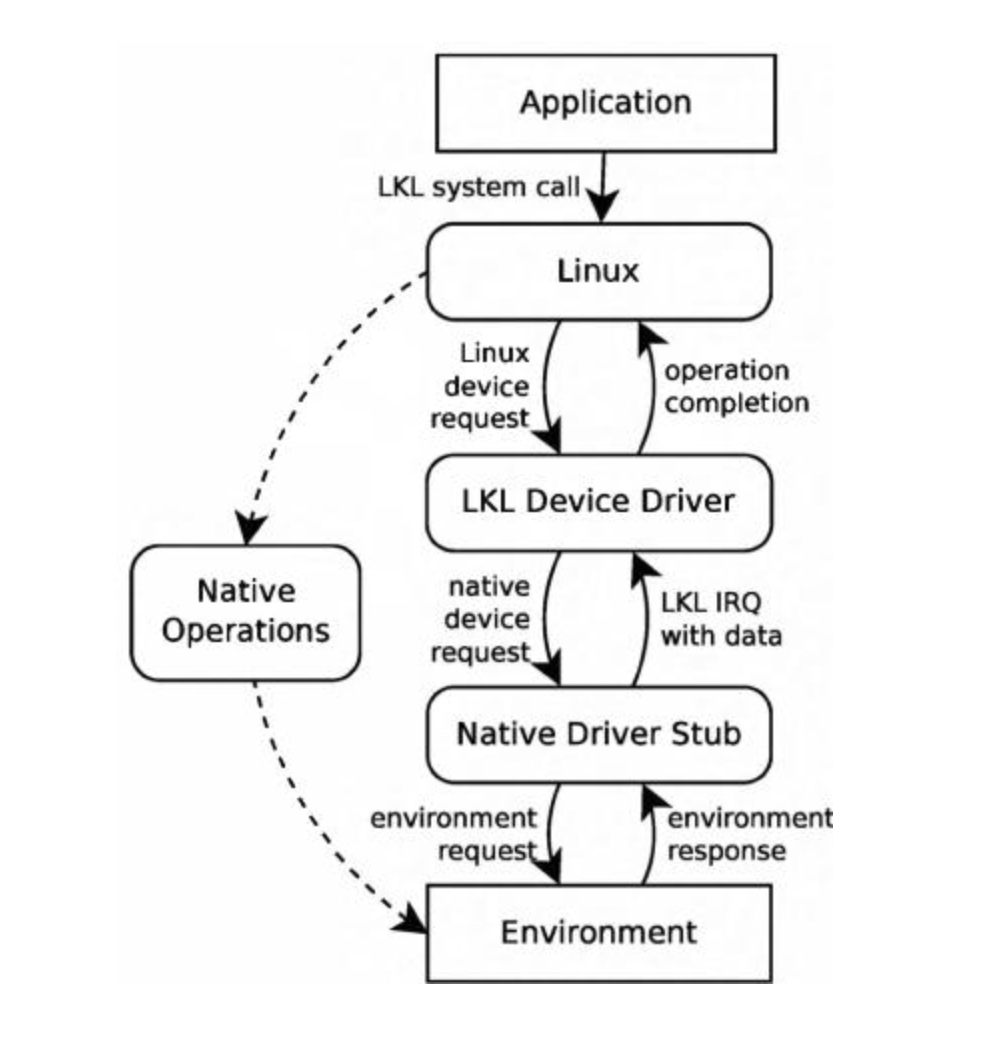
The Request:
- An application makes a request (e.g., read) through LKL’s safe, interrupt-based system call API, then sleeps.
- The LKL kernel processes the request and calls out to a native stub (a callback function provided by the application).
- This stub executes the actual I/O operation using the host OS’s functions.
The Responses:
- When the host I/O is finished, the native stub is notified.
- The stub triggers a simulated IRQ back into LKL to signal completion.
- LKL handles this completion and wakes up the original application thread with the data or result.
Application
Target: reuse the original, high-quality Linux kernel code as a library
Code:
arch/lkl: 实现内核到用户空间的移植,提供内核运行环境
tools/lkl: 提供用户接口,封装成库和工具供应用程序使用
User Space TCP
Container
UINTR
Mechanism
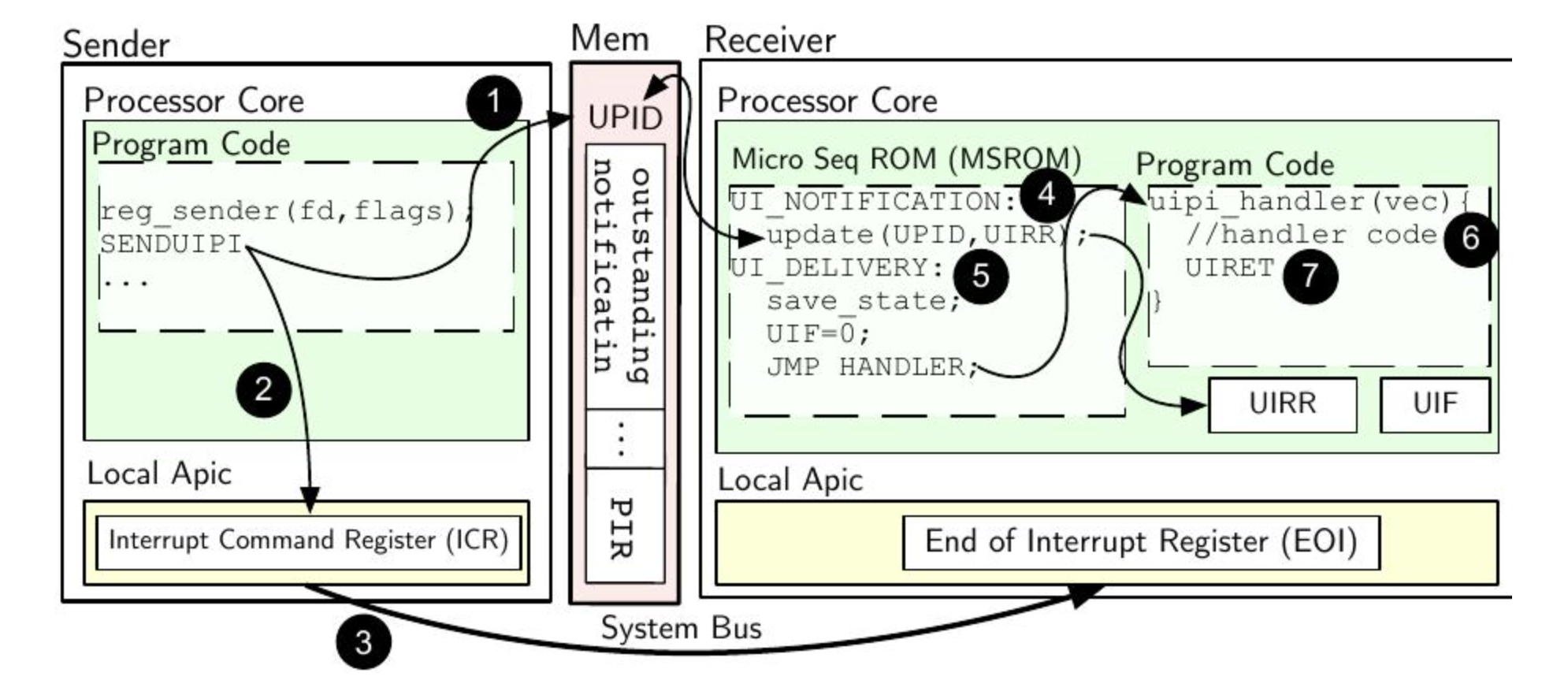
1. Setup
- Receiver: Creates a UPID and sets the UIHANDLER register to point to its user-space handler code.
- Sender: Creates a UITT (address book) that points to the receiver’s UPID address.
- System: The UINV register is configured with a special number to identify all incoming user interrupts.
2. Sending Process
- SENDUIPI writes a message to the receiver’s PIR and sends a IPI to the receiver’s CPU core.
3. Receiving Process
The hardware checks the incoming IPI’s number. If it matches the UINV register, it knows it’s a user interrupt.
It then jumps directly to the user-space handler code, completely bypassing the kernel.
The handler executes the UIRET instruction.
Application
The problems:
- high tail latency -> preempt -> based on regular interrupts still incur high overheads
- the CPU performance is becoming the major bottleneck. -> kernel-bypassing
- switching a core between two applications, the CPU core needs to trap into the Linux kernel to switch the address space.(IPI)
- Limitations of User-Level Notification(signal poll…)
The solutions,Related works:
Libpreemptible(function) a user-level threading library
Skyloft(user thread) a kernel module
Vessel(uProcess) a standalone auxiliary program
PreemptDB(transactions) a DB engine
Limitations:
- not support timer and extern interrupt(xUI)
Questions
LibOS is a library or an OS?
- it is passive code that only runs in direct response to a call from the application within the same process.
LKL is a form of libOS?
- LKL completely dependent on or cooperate with hostOS
how to Run the Uintr code
relationship between LKL and UINTR
Paper - Code